3M Prevena Therapy for orthopaedic surgery
Enhanced orthopaedic surgery outcomes with Prevena Therapy
A peer-reviewed meta-analysis of 12 studies for orthopaedic joint replacement procedures demonstrated Prevena Therapy helped significantly reduce the risk of various surgical site complications (SSCs) while helping to improve health economic outcomes compared to standard-of-care dressings.¹
Reduction in SSCs¹,*
8 studies; p<0.001†
Reduction in surgical site infections (SSIs)¹,*
7 studies; p=0.016†
Reduction in seromas¹,*
3 studies; p=0.008†
*Relative risk reduction based on risk ratios reported in this study.
†Calculation(s) are derived based on the relative patient group incidence rate reporting in this study. Statistically significant (p<0.05).
See full indications for use and limitations at hcbgregulatory.3M.com.
Proactive risk management (PRM)
Access comprehensive resources to implement PRM into your practice with Prevena Therapy, helping to elevate your standard of patient care with proven postoperative benefits.
Prevena Therapy video resources
3M™ Prevena™ Therapy Tips and Tricks Video Orthopedic Hip, EN US
8 Videos
Explore more
Abstracts
Discover abstracts from prominent research papers on topics related to Prevena Therapy, offering valuable scientific findings and perspectives.
- The effectiveness of closed-incision negative-pressure therapy versus silver-impregnated dressings in mitigating surgical site complications in high-risk patients after revision knee arthroplasty: The PROMISES randomized controlled trial
- Negative pressure wound therapy to prevent seromas and treat surgical incisions after total hip arthroplasty
- Closed Incision Negative Pressure Therapy vs Standard of Care Over Closed Knee and Hip Arthroplasty Surgical Incisions in the Reduction of Surgical Site Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies
- Use of closed incisional negative pressure wound therapy after revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in patients at high risk for infection: A prospective, randomized clinical trial
- Comparison of surgical site complications with negative pressure wound therapy vs silver impregnated dressing in high-risk total knee arthroplasty patients: A matched cohort study
- Cost-effectiveness of closed incision negative pressure therapy for surgical site management after revision total knee arthroplasty: Secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial
- Closed-incision negative-pressure therapy versus antimicrobial dressings after revision hip and knee surgery: A comparative study
- A risk-stratification algorithm to reduce superficial surgical site complications in primary hip and knee arthroplasty
- Closed incision negative pressure therapy effects on postoperative infection and surgical site complication after total hip and knee arthroplasty
NOTE:
Specific indications, limitations, contraindications, warnings, precautions and safety information exist for these products and therapies. Please consult a clinician and product instructions for use prior to application. This material is intended for healthcare professionals.
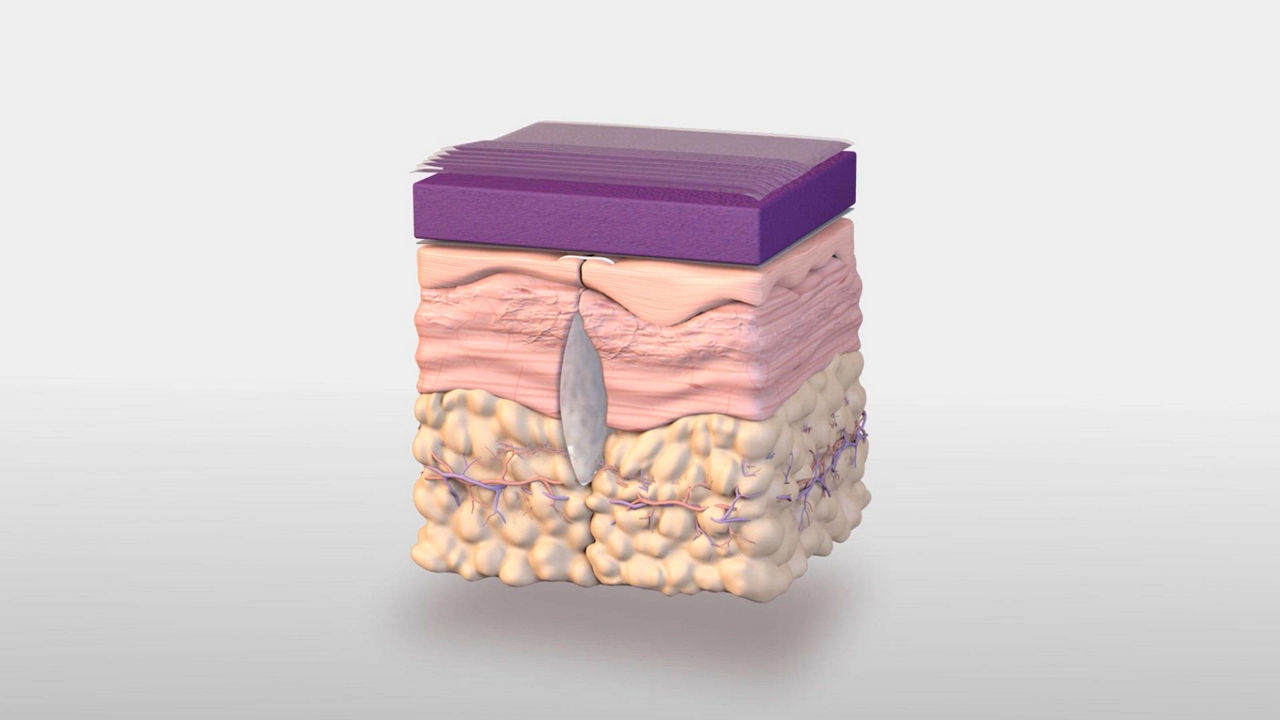
The 3M™ Prevena™ Plus 125 Therapy Unit, when used with 3M™ Prevena™ Dressings (3M™ Prevena™ Plus Incision Management System), is intended to manage the environment of closed surgical incisions and surrounding intact skin in patients at risk for developing post-operative complications, such as infection, by maintaining a closed environment via the application of a negative pressure wound therapy system to the incision.
Prevena Dressing used with Prevena Therapy Units: PREVENA™ 125 and PREVENA PLUS™ 125 Therapy Units manage the environment of closed surgical incisions and remove fluid away from the surgical incision via the application of -125mmHg continuous negative pressure. When used with legally marketed compatible PREVENA™ dressings for up to seven days, PREVENA™ 125 and PREVENA PLUS™ 125 Therapy Units are intended to aid in reducing the incidence of seroma; and in patients at high risk for post-operative infections, aid in reducing the incidence of superficial surgical site infection in Class I and Class II wounds.
Limitations:
- The device is not intended to treat surgical site infection or seroma.
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric population (<22 years old) have not been evaluated.
- Safety and effectiveness in Class III (Contaminated) and Class IV (Dirty/Infected) wounds have not been demonstrated. Furthermore, Class IV surgical wounds are not expected to be closed primarily, and the subject device should only be used on closed surgical incisions.
- The device has not been demonstrated to reduce deep incisional and organ space surgical site infections.
- The device has not been demonstrated to be effective in reducing the incidence of surgical site infection and seroma in all surgical procedures and patient populations; therefore, the device may not be recommended for routine use to reduce the incidence of surgical site infection and seroma.
- Please refer to the ‘Summary of Clinical Information’ section for the specific surgical procedures and patient populations included in the clinical studies. Surgeons should continue to follow the ‘Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection’2 and the ‘American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines’3 for best practices in preventing surgical site infection. US FDA Cleared: Dressings/ Systems (Prevena Dressings used with compatible Solventum NPWT units - ActiVAC, Ulta, and RX4) and applicable OUS countries that leverage US Indication: The PREVENA™, PREVENA PLUS™, PREVENA DUO™, and PREVENA RESTOR™ Incision Management Systems are intended to manage the environment of surgical incisions that continue to drain following sutured or stapled closure by maintaining a closed environment and removing exudates via the application of negative pressure wound therapy.
References:
- Cooper HJ, Silverman RP, Collinsworth A, Bongards C, Griffin L. Closed Incision Negative Pressure Therapy vs Standard of Care Over Closed Knee and Hip Arthroplasty Surgical Incisions in the Reduction of Surgical Site Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Arthroplasty Today. 2023;21:101120. Published 2023 Apr 3. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2023.101120
- Berríos-Torres, S. I., Umscheid, C. A., Bratzler, D. W., Leas, B., Stone, E. C., Kelz, R. R., Reinke, C. E., Morgan, S., Solomkin, J. S., Mazuski, J. E., Dellinger, E. P., Itani, K. M., Berbari, E. F., Segreti, J., Parvizi, J., Blanchard, J., Allen, G., Kluytmans, J. A., Donlan, R., & Schecter, W. P. (2017). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, 2017. JAMA Surgery, 152(8), 784. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904
- Ban, K. A., Minei, J. P., Laronga, C., Harbrecht, B. G., Jensen, E. H., Fry, D. E., Itani, K. M. F., Dellinger, P. E., Ko, C. Y., & Duane, T. M. (2017). American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 update. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 224(1), 59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.10.029