3M Prevena Therapy for vascular surgery
Enhanced vascular surgery outcomes with Prevena Therapy
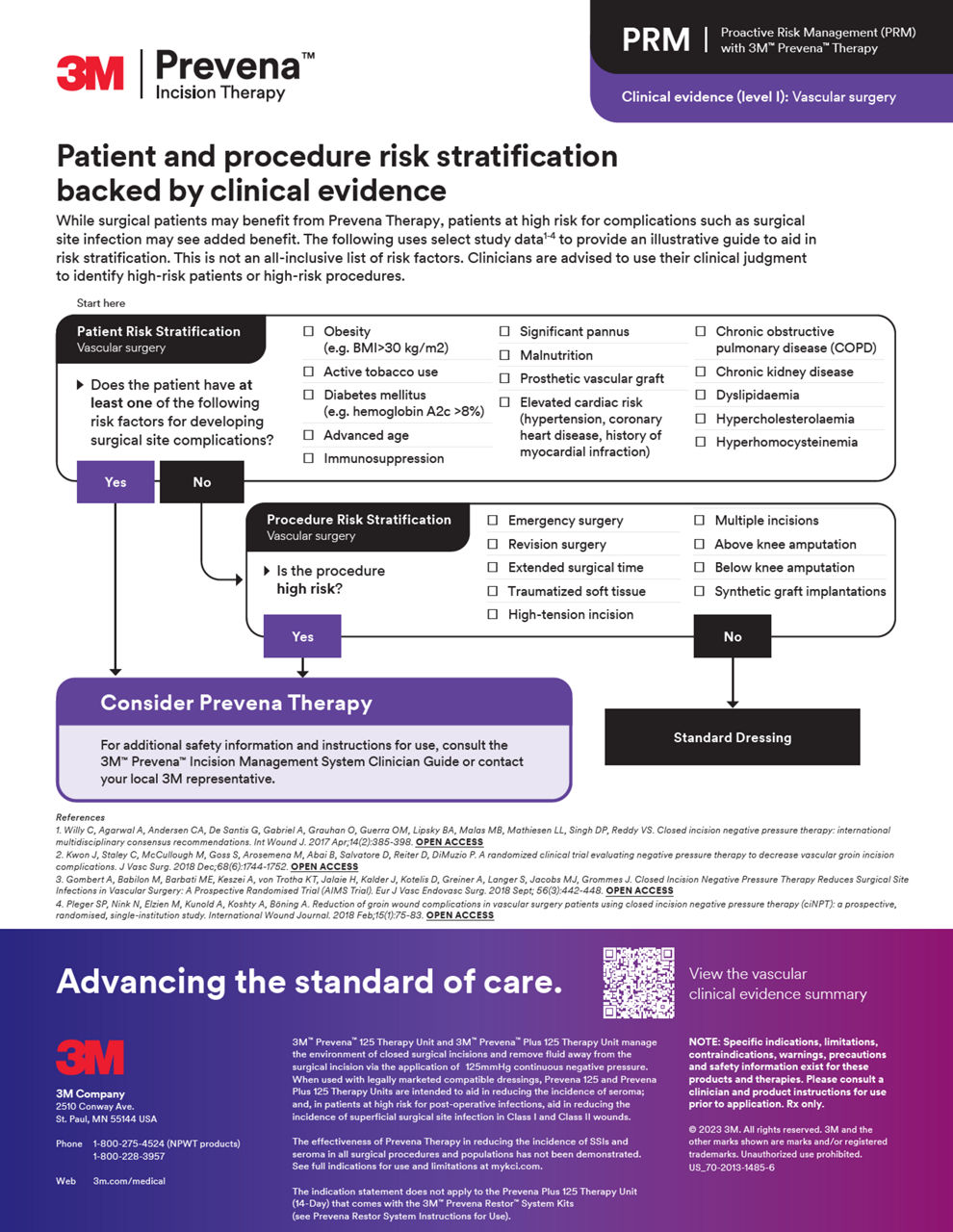
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 6 studies for vascular surgery procedures demonstrated that Prevena Therapy helped significantly reduce the risk of various surgical site infections (SSIs), revision surgeries and shorter hospital length of stay.
*Risk-reduction is calculated based on Risk Ratio derived from related Odd Ratios and Prevalence Rate.
†Calculation(s) are derived based on the relative patient group incidence rate reporting in this study. Statistically significant (p<0.05).
See full indications for use and limitations at hcbgregulatory.3M.com.
Proactive risk management (PRM)
Access comprehensive resources to implement PRM into your practice with Prevena Therapy, helping elevate your standard of patient care with proven postoperative benefits.
Prevena Therapy video resources
3M™ Prevena™ Therapy Tips and Tricks Video Vascular Groin, EN, US
Explore more
Abstracts
Discover abstracts from prominent research papers on topics related to Prevena Therapy, offering valuable scientific findings and perspectives.
- A randomized clinical trial evaluating negative pressure therapy to decrease vascular groin incision complications
- Utilizing closed incisional negative pressure therapy reduces peripheral bypass infection rates without increasing costs
- Closed incision negative pressure therapy reduces surgical site infections in vascular surgery: A prospective randomised trial (AIMS trial)
- Closed incision negative pressure wound therapy may decrease wound complications in major lower extremity amputations
- Deep learning-based risk model for best management of closed groin incisions after vascular surgery
- Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of prophylactic negative pressure therapy for groin wounds in vascular surgery
- Reduction of groin wound complications in vascular surgery patients using closed incision negative pressure therapy (ciNPT): a prospective, randomised, single-institution study
NOTE:
Specific indications, limitations, contraindications, warnings, precautions and safety information exist for these products and therapies. Please consult a clinician and product instructions for use prior to application. This material is intended for healthcare professionals.
Indication(s) For Use / Intended Use:
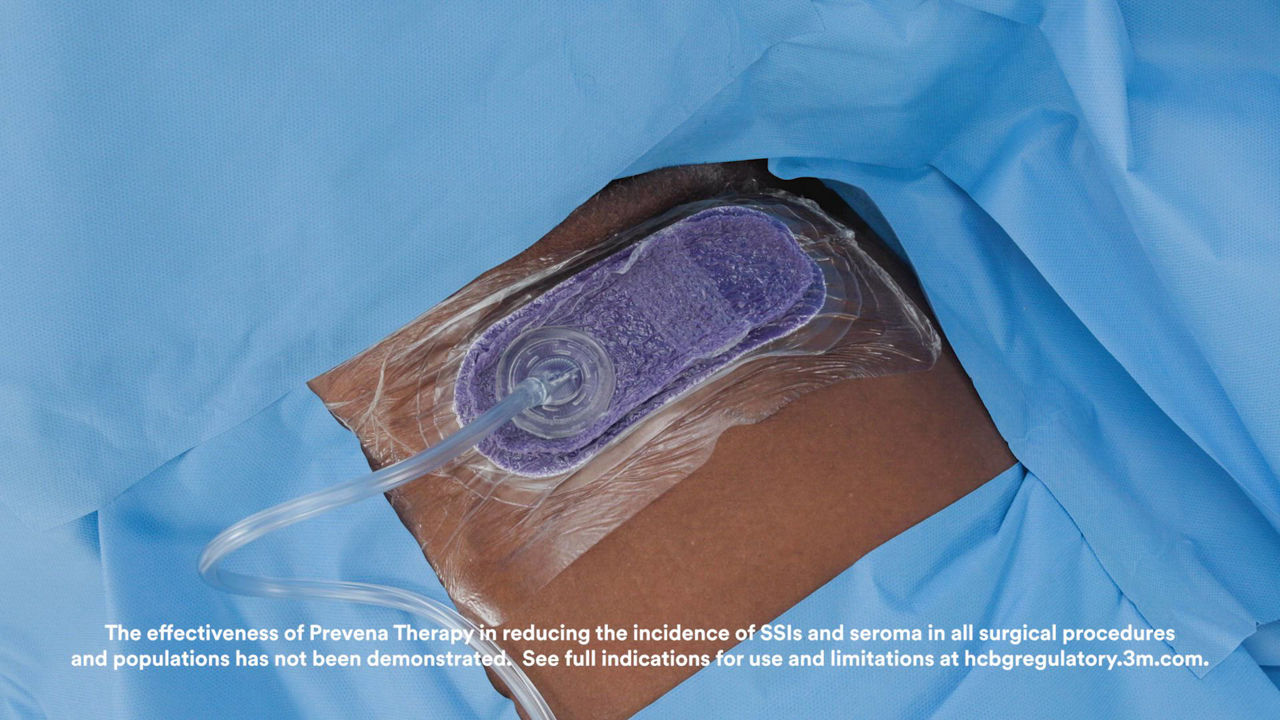
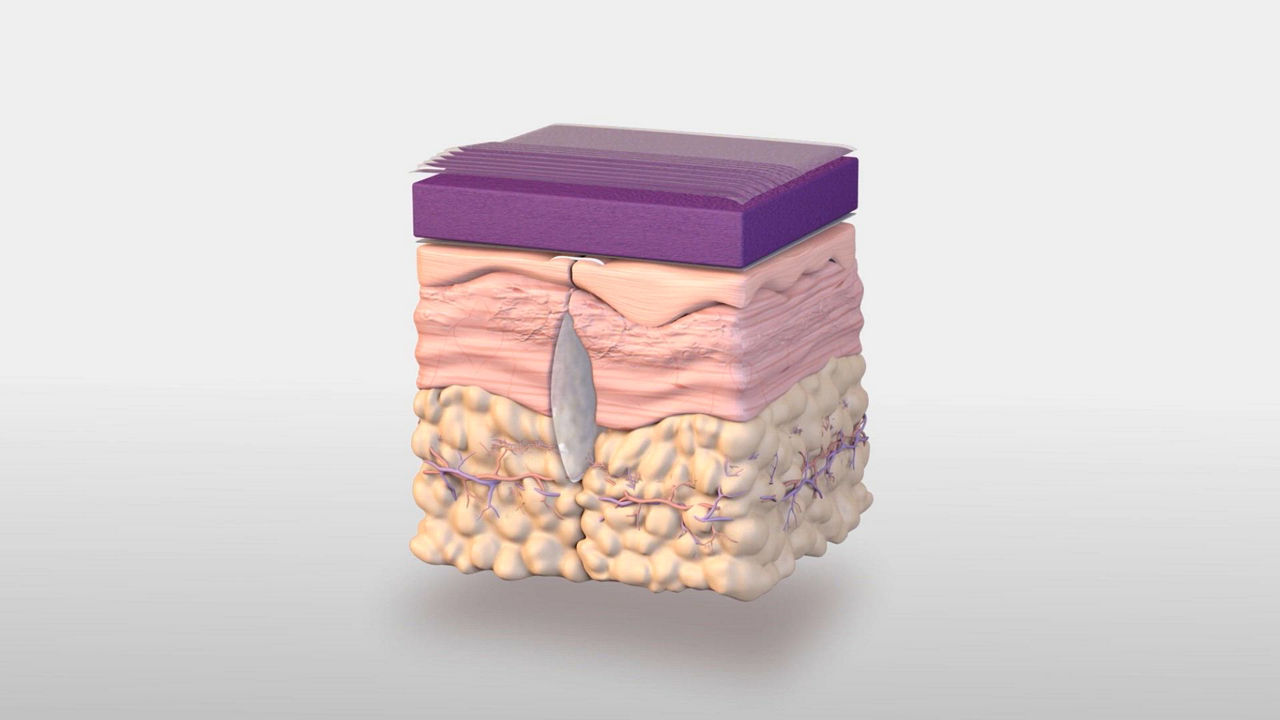
The 3M™ Prevena™ Plus 125 Therapy Unit, when used with 3M™ Prevena™ Dressings (3M™ Prevena™ Plus Incision Management System), is intended to manage the environment of closed surgical incisions and surrounding intact skin in patients at risk for developing post-operative complications, such as infection, by maintaining a closed environment via the application of a negative pressure wound therapy system to the incision.
See full indications and limitations for use at hcbgregulatory.3m.com
References:
- Antoniou G, Onwuka C, Antoniou S et al. Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of prophylactic negative pressure therapy for groin wounds in vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg 2019; 70 (5):1700-1710.
- Berríos-Torres, S. I., Umscheid, C. A., Bratzler, D. W., Leas, B., Stone, E. C., Kelz, R. R., Reinke, C. E., Morgan, S., Solomkin, J. S., Mazuski, J. E., Dellinger, E. P., Itani, K. M., Berbari, E. F., Segreti, J., Parvizi, J., Blanchard, J., Allen, G., Kluytmans, J. A., Donlan, R., & Schecter, W. P. (2017). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, 2017. JAMA Surgery, 152(8), 784. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904
- Ban, K. A., Minei, J. P., Laronga, C., Harbrecht, B. G., Jensen, E. H., Fry, D. E., Itani, K. M. F., Dellinger, P. E., Ko, C. Y., & Duane, T. M. (2017). American College of Surgeons and Surgical Infection Society: Surgical Site Infection Guidelines, 2016 update. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 224(1), 59–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.10.029